The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s (CDC) state-based disability and health programs inform policy and practice at the state level. These programs ensure that individuals with disabilities are included in ongoing state disease prevention, health promotion, and emergency response activities.
CDC supports 18 state-based programs to promote equity in health, prevent chronic disease, and increase the quality of life for people with disabilities. Each program customizes its activities to meet its state’s needs, which broadens expertise and information sharing among states.
The programs’ goals are to:
- Enhance program infrastructure and capacity.
- Improve state level surveillance and monitoring activities.
- Increase awareness of health-related disability policy initiatives.
- Increase health promotion opportunities for people with disabilities.
- Improve access to health care services for people with disabilities.
- Improve emergency preparedness for people with disabilities.
- Effectively monitor and evaluate program activities.
The goals of the state disability and health programs align with those of Healthy People 2020 related to disability:
- Removing barriers to participation in social, spiritual, recreational, community and civic activities.
- Improving access to primary care, and health and wellness programs.
- Identifying people with disabilities in data systems.
- Increasing surveillance and health promotion programs.
- Providing graduate-level courses in disability and health.
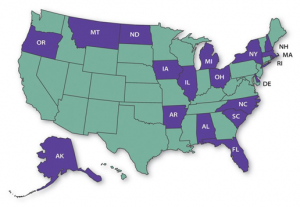
States funded by CDC for Disability and Health Programs:
- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arkansas
- Delaware
- Florida
- Illinois
- Iowa
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Montana
- New Hampshire
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oregon
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
Alabama
Program activities include:
- Promoting inclusion of persons with disabilities in all aspects of policy development, planning, and execution of state based public health programs.
- Using Federally Qualified Healthcare Centers to assist with capacity assessment of ability to meet the needs of those with disabilities and determine barriers to inclusiveness.
- Increasing health promotion opportunities for persons with disabilities through adaptation of existing public health programs, such as Scale Back Alabama, and increasing the number of children with disabilities who participate in mainstream physical education and after-school programs.
Alaska
Program activities include:
- Developing accurate and timely outreach for Alaskans experiencing disability and their care providers.
- Building the capacity of a cross-agency disability advisory council that reviews and evaluates program activities, assists with sustainability plans, and provides recommendations for policy change.
- Providing technical assistance, training, and other support for existing community-wide initiatives designed to improve the health of Alaskans experiencing disability.
The Alaska Disability and Health Program is a collaboration between the State of Alaska’s Department of Health and Social Services, Division of Public Health, Section of Women’s, Children’s, and Family Health and the Governor’s Council on Disabilities and Special Education, and is housed in the Division of Public Health.
Arkansas
Program activities include:
- Enhancing program infrastructure and capacity through the expansion and support of an Advisory Board and increasing the representation of individuals with disabilities on public health program committees.
- Improving state-level surveillance and monitoring by conducting a statewide needs assessment to look at the health status and access of people with disabilities, developing documents comparing demographics and health disparities of Arkansas and the U.S.
- Increasing awareness of health-related disability policy initiatives through Disability Policy Summits; educating and supporting advocates on proposed policy initiatives and disseminating information to policy makers.
- Increase health promotion opportunities for people with disabilities by supporting training that maximizes the health of people with disabilities and implementing health awareness and education campaigns.
- Improving access to health care for people with disabilities by looking at the accessibility of healthcare facilities, and educating healthcare professionals through continued education, as well as internship placement for students in 11 different health related disciplines.
- Improving emergency preparedness among people with disabilities by reviewing state emergency plans for accessibility, involving people with disabilities in county level planning, providing training, and ensuring shelter access by identifying and surveying pre-designated shelter sites.
The Arkansas Disability and Health Program is housed in the Partners for Inclusive Communities at the University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences.
Delaware
Program activities include:
- Creating systems-level change through active participation on statewide councils, committees, and workgroups that are addressing health and disability issues and implementation of goals and objectives of the Plan for Action, A Strategic Plan for Delaware to Promote Health and Prevent Secondary Health Conditions in Individuals with Disabilities.
- Providing technical assistance for health care, fitness, and recreation providers and facilities to improve accessibility and inclusion of individuals with disabilities in health examinations, exercise programs, and recreation activities.
- Providing education, awareness raising, and resources sharing through the program’s interactive website www.gohdwd.org and email newsletters to individuals with disabilities, family members, professionals, policymakers, and legislators.
The Delaware Disability and Health Program, Healthy Delawareans with Disabilitiesis housed in the Center for Disabilities Studies at the University of Delaware.
Florida
Program activities include:
- Promoting breast cancer awareness and encouraging recommended screening among women 40 years of age or older who have a disability (the Right to Know Campaign) with partners such as the Florida Centers for Independent Living and the Florida Area Health Education Centers.
- Increasing the capacity of health care providers in Florida to provide quality health care to people with disabilities by training medical students, and medical and allied health professionals.
- Increasing the quantity and quality of disability and health-related data in Florida and providing the epidemiologic capacity to analyze these data.
The Florida Disability and Health Program is housed in the Office of Disability and Health at the University of Florida.
Illinois
Program activities include:
- Monitoring the health status and health-related behaviors of people with disabilities, and sustaining and expanding the statewide infrastructure to prevent secondary conditions and promote the health of people with disabilities in Illinois.
- Increasing evidence-based health promotion and prevention opportunities and resources available for people with disabilities to promote healthy lifestyles and reduce the risk of chronic disease and secondary conditions.
- Assisting health professionals to gain the knowledge and tools necessary to work effectively with people with a disability to increase the availability and accessibility of health promotion and prevention services, interventions, and resources.
The Illinois Disability and Health Program is housed in the Illinois Department of Public Health.
Iowa
Program activities include:
- Developing a statewide network of community providers that offer the Living Well with a Disability intervention program.
- Identifying evidence-based strategies to increase awareness and education opportunities for health professionals.
- Promoting accessible health care and support services to increase independence among people with disabilities.
The Iowa Disability and Health Program is housed in the Iowa Department of Public Health.
Massachusetts
Program activities include:
- Designing and implementing training and technical assistance for health care providers and public health programs on the Americans with Disabilities Act to ensure inclusion of people with disabilities in state funded programs, services, and activities.
- Providing the knowledge base needed to design programs related to healthy aging, health and disability, and secondary health conditions.
- Working with state agencies and community partners to identify, implement, and evaluate evidence-based health promotion programs among older adults and people with disabilities (for example, the Stanford Chronic Disease Self-Management Program).
The Massachusetts Disability and Health Program is housed in the Massachusetts Department of Public Health.
Michigan
Program activities include:
- Implementing the Stanford Chronic Disease Self-Management Program, known as the Personal Action Toward Health Program (PATH), in Michigan.
- Analyzing surveillance data on disability using the Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System (BRFSS), including health status and chronic disease prevalence among people with disabilities, and the health effects of caregiving.
- Promoting the inclusion of people with disabilities in existing public health programs.
The Michigan Health Promotion for People with Disabilities Program is housed in the Michigan Department of Community Health.
Montana
Program activities include:
- Recruiting, training, and supporting disability advisors to participate in Montana Department of Public Health and Human Services advisory groups and integrate disability and health into public health planning and evaluation processes.
- Recruiting, training, and supporting state disability leaders to assess and improve the accessibility of community health and fitness programs.
- Conducting Living Well with a Disability, an eight-week peer-facilitated, health promotion workshop with Montana’s four Centers for Independent Living.
The Montana Disability and Health Program is a collaboration between the Montana Department of Public Health and Human Services and the University of Montana Rural Institute, a Center for Excellence in Disability Education, Research, and Service.
New Hampshire
Program activities include:
- Training students, self-advocates, families and professionals through coursework, seminars, workshops and conferences.
- Providing technical assistance to organizations and individuals to improve their capacity to include all citizens.
- Serving as a resource for information to policymakers and government officials.
- Disseminating information to families, consumers, community members and professionals via books, monographs, articles, videos, newsletters, the Internet and press coverage, including TV, radio, newspapers and consumer forums.
- Conducting applied research to better understand and address the needs of individuals with disabilities.
- Engaging in collaborative activities and joint projects with organizations that share common goals.
The Institute on Disability (IOD) is housed within New Hampshire’s University Center for Excellence on Disability (UCED).
New York
Program activities include:
- Implementing the New York State Department of Health (NYSDOH) Center for Community Health Inclusion Policy, which requires all Center for Community Health programs to ensure accessibility and inclusion for people with disabilities throughout all funding opportunities. The proposed activities to implement inclusive local and statewide public health programs must also include an evaluation of the effect and reach of the policy.
- Educating and training NYSDOH program managers, primary program implementation staff, NYSDOH contractors and partners about the health disparities experienced by people with disabilities and providing strategies, resources, and potential partners that will enable the integration of people with disabilities in their program areas.
- Supporting an advisory body comprising individuals with disabilities, other state agencies, community-based organizations, and providers to inform program activities, as well as representing multiple external agency advisory committees to direct consideration of health care and health promotion needs of people with disabilities.
The New York Disability and Health Program is housed in the New York State Department of Health.
North Carolina
Program activities include:
- Supporting the collection, analysis, and dissemination of data on people with an intellectual or developmental disability, or both, to better assess the health status of North Carolina adults.
- Promoting accessible environments to support full community participation and engaging people with disabilities by developing accessibility checklists for health care practices and by providing training on adaptive and inclusive fitness and how to remove barriers to fitness facilities.
- Increasing access to domestic violence and sexual assault services for people with disabilities with the implementation of adaptive equipment and enhanced disability awareness among domestic violence and sexual assault agencies.
The North Carolina Disability and Health Program is housed in the North Carolina Office on Disability and Health, and is a collaboration between the Division of Public Health of the North Carolina Department of Health and Human Services and the Frank Porter Graham Child Development Institute at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill.
North Dakota
Program activities include:
- Forming a consumer-driven advisory council that reviews the progress of the program activities, reviews data related to the health of people with disabilities, assists with development of a strategic plan, and provides recommendations for addressing issues related to the health and wellness of North Dakota citizens with disabilities.
- Reducing health disparities in the areas of obesity, diabetes, and tobacco use among people with disabilities.
- Ensuring people have accurate information on disability and health issues and promoting communication, planning, and implementation of health- and disability-related services across service systems.
The North Dakota Disability and Health Program, named the Disability Health Project, is a collaboration between the North Dakota Center for Persons with Disabilities at Minot State University; the Center for Rural Health at the University of North Dakota; and the North Dakota State Health Department, Division of Chronic Disease, Office for the Elimination of Health Disparities.
Ohio
Program activities include:
- Improving state-level surveillance and monitoring activities with epidemiologic expertise from the Government Resource Center (GRC).
- Advancing health-related disability policy initiatives in Ohio.
- Promoting the health of people with disabilities through demonstration projects and train-the-trainer sessions.
- Improving access to health care for people with disabilities through our partnership with the Ohio Association of Community Health Centers.
- Revising Ohio Emergency Management Plans and committees to be inclusive of people with disabilities, increasing the number of PWD who have emergency plans, training first responders on the needs of PWD, and improving the accessibility of emergency shelters.
The Ohio Disability and Health Program is composed of the Ohio Department of Health, the Ohio State University Nisonger Center, the University of Cincinnati UCEDD, and the Ohio Colleges of Medicine Government Resource Center (GRC).
Oregon
Program activities include:
- Conducting Healthy Lifestyles workshops for people with disabilities (in English and Spanish) to improve quality of life in partnership with the Centers for Independent Living and other disability organizations.
- Implementing the Right to Know campaign and breast health education events, providing mammography technologist training, and assessing Oregon’s mammography clinics to improve breast cancer awareness and screening among women with disabilities.
- Providing individualized emergency preparedness training for Oregonians with disabilities as well as working with key community and state partners to ensure that emergency preparedness planning and training efforts include topics relevant to the health and safety of people with disabilities.
The Oregon Disability and Health Program is housed in the Oregon Office on Disability and Health at Oregon Health and Science University.
Rhode Island
Program activities include:
- Promoting the health and wellness for people with disabilities through inclusive self-management, evidence-based programs.
- Monitoring, supporting and implementing effective healthcare transition from pediatric to adulthood within a positive youth development framework that promotes self-determination and an activated patient model.
- Providing professional development for practitioners working with people with disabilities, including training, targeted technical assistance, and access to assistive technology.
- Addressing special needs of people with disabilities in health promotion programs, health strategic planning, emergency preparedness, preventative health screening programs, and healthcare facility access.
- Increasing access to quality of health-related data of people with disabilities in Rhode Island and using epidemiology and evaluation analysis to monitor the health disparities.
The Rhode Island Disability and Health Program is housed in the Office of Special Needs of the Health Disparities and Access to Care Team at the Rhode Island Department of Health.
South Carolina
Program activities include:
- Increasing the knowledge of professionals and paraprofessionals in South Carolina to meet the preventive, primary, and secondary health needs of people with disabilities.
- Conducting ongoing surveillance with Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System (BRFSS) and administrative datasets as secondary sources via the South Carolina Disability Cube Project.
- Working to achieve more livable communities for people with disabilities by facilitating access to primary care physician offices, increasing access to fitness and recreation facilities, and working with community planning agencies to improve outdoor space using principals of universal design.
The South Carolina Disability and Health Program is housed in the University of South Carolina School of Medicine.